In today’s world of advanced automation and precision engineering, hobbyists and professionals alike are leveraging cutting-edge tools to bring their creative visions to life. Whether it’s crafting intricate parts with a CNC controller, enhancing automation with a PoKeys57U, building a delicate ecosystem in a DIY orchidarium, or ensuring clean wire management with a flat cable cutter, these technologies are revolutionizing how we approach projects.
This article explores four key components that can elevate your DIY and professional work. We’ll start with the CNC controller, the brain behind precision machining, before diving into the versatile PoKeys57U for automation control. Then, we’ll shift to the delicate art of constructing a DIY orchidarium, and finally, examine the importance of a flat cable cutter in maintaining clean and efficient wiring setups.
By the end, you’ll understand how these tools interconnect in modern fabrication and automation, empowering you to take your projects to the next level.
The CNC Controller – The Brain of Precision Machining
At the heart of every modern CNC machine lies the CNC controller, a sophisticated device that translates digital designs into precise physical movements. Whether you’re working with a milling machine, a lathe, or a 3D printer, the CNC controller is what ensures accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency in automated fabrication.
How a CNC Controller Works
A CNC controller receives instructions from computer-aided design (CAD) or computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software in the form of G-code. This code dictates the exact coordinates, speeds, and toolpaths the machine must follow. The CNC controller then processes these commands, sending electrical signals to stepper or servo motors that drive the machine’s axes.
Advanced CNC controllers also incorporate real-time feedback systems, such as encoders, to monitor and adjust positioning dynamically. This closed-loop control minimizes errors, ensuring that even complex geometries are machined with tight tolerances.
Types of CNC Controllers
There are several types of CNC controllers, each suited for different applications:
- Standalone Controllers – Dedicated units like Mach3, LinuxCNC, or GRBL-based boards, often used in hobbyist and small-scale CNC machines.
- Industrial PC-Based Controllers – High-performance systems running on industrial computers, common in large-scale manufacturing.
- Open-Source Controllers – Arduino or Raspberry Pi-based solutions, popular in DIY CNC projects due to their flexibility and affordability.
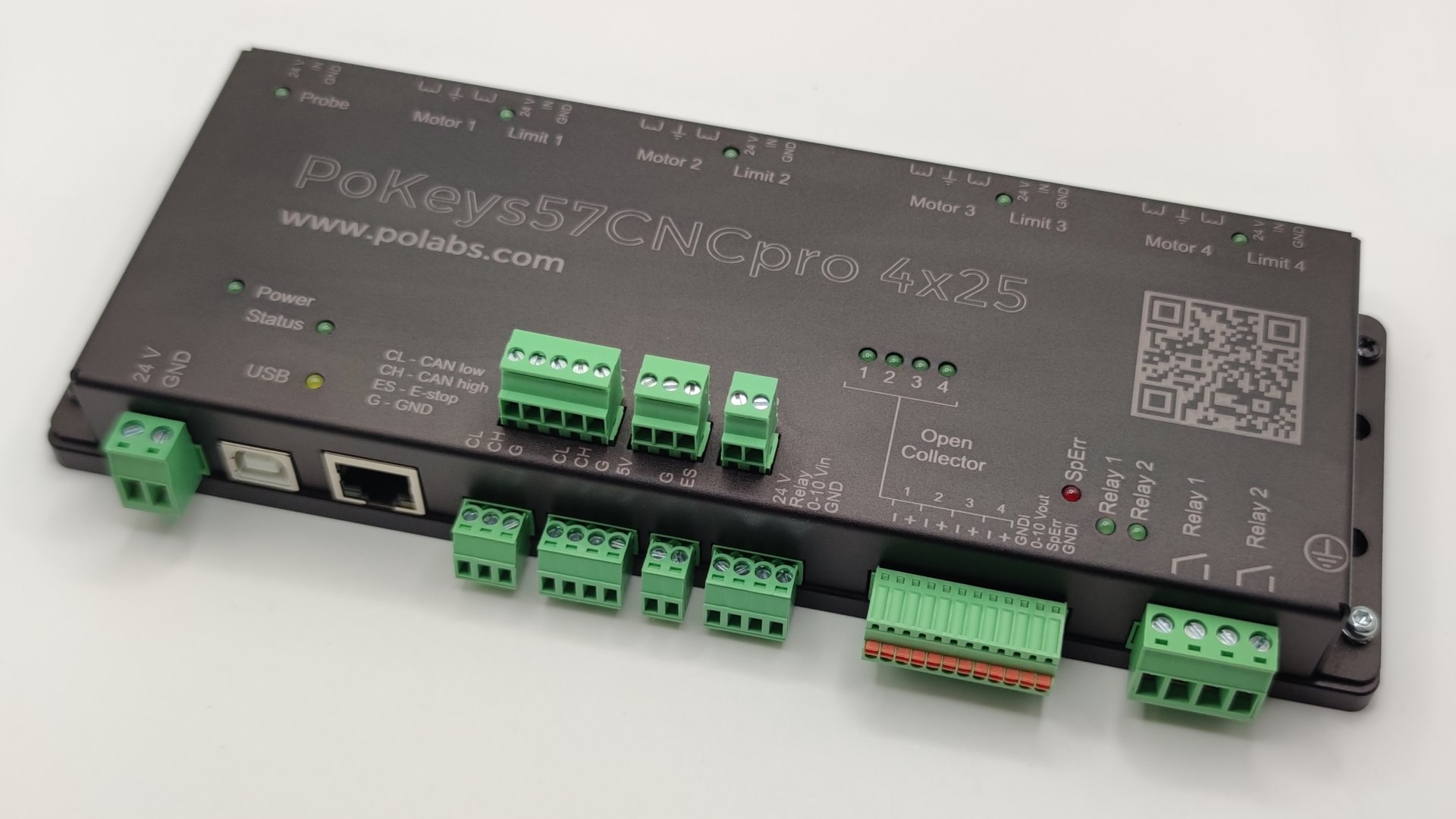

Key Features to Look For
When selecting a CNC controller, consider:
- Compatibility – Does it support your machine’s motors and drivers?
- Software Integration – Can it work with your preferred CAD/CAM programs?
- Expandability – Are there additional I/O ports for sensors or automation?
- User Interface – Is it intuitive for beginners, or does it require advanced knowledge?
Why the CNC Controller is Indispensable
Without a reliable CNC controller, even the most robust CNC machine would be useless. It bridges the gap between digital designs and physical parts, enabling everything from rapid prototyping to mass production. As CNC technology evolves, CNC controllers are becoming smarter, incorporating AI-driven optimizations and cloud-based monitoring for even greater efficiency.
In the next chapter, we’ll explore how the PoKeys57U can further enhance automation by adding programmable control to your CNC or other DIY projects.
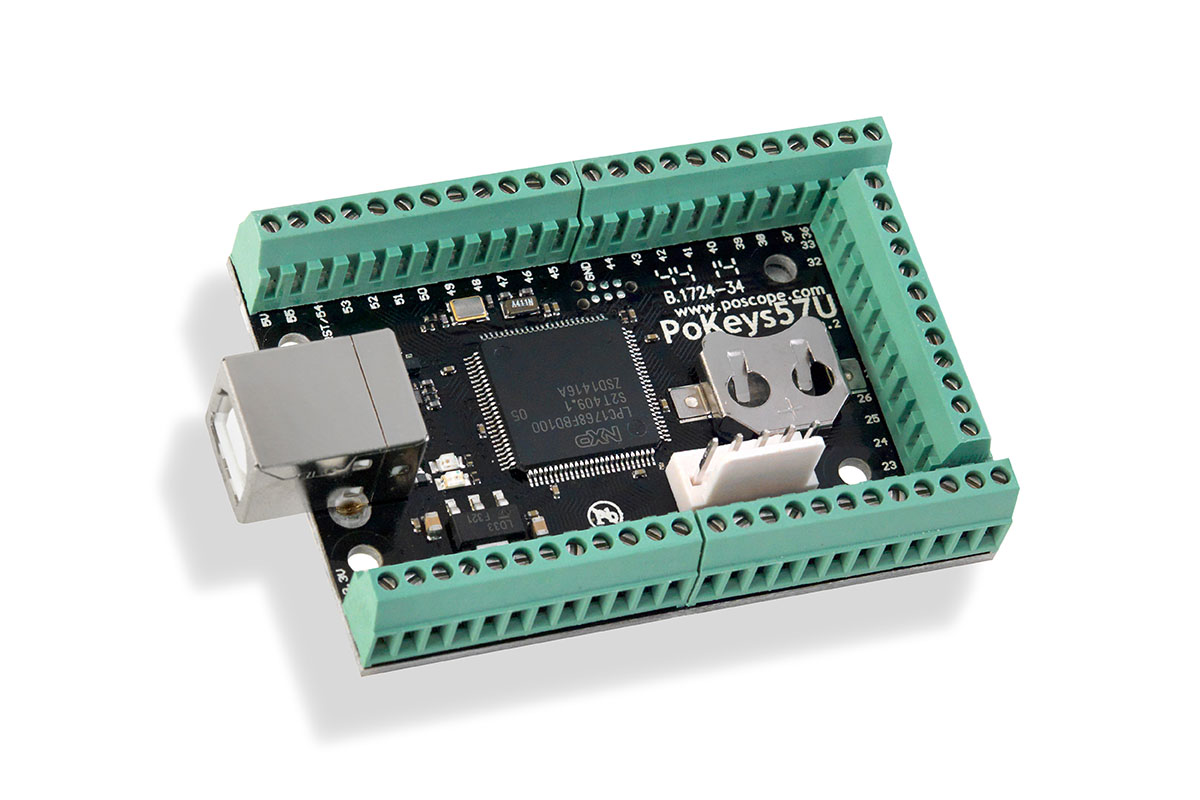
PoKeys57U – The Intelligent Hub for Custom Automation
While CNC controllers excel at precision motion control, many advanced projects demand a more flexible approach to automation. This is where the PoKeys57U enters the picture – a compact yet remarkably capable USB interface device that bridges the gap between simple microcontrollers and industrial control systems. With its versatile I/O capabilities and real-time responsiveness, the PoKeys57U has become an indispensable tool for makers and engineers alike.
The Power of Programmable Control
What sets the PoKeys57U apart is its ability to handle multiple automation tasks simultaneously. The device features 56 fully configurable I/O pins that can be dynamically assigned as digital inputs or outputs, PWM channels, or analog inputs. This flexibility allows it to interface with everything from simple switches to complex motor drivers. The built-in encoder support makes it particularly valuable for motion control applications, while its keyboard emulation mode enables seamless integration with existing software.
Unlike generic development boards, the PoKeys57U is designed specifically for real-world automation scenarios. Its deterministic response times, often as fast as 1ms, ensure reliable operation in time-critical applications. The device maintains this performance while communicating over standard USB, eliminating the need for specialized interface cards or complex driver configurations.
Seamless Integration with Workshop Systems
In practical applications, the PoKeys57U often serves as the nervous system of a workshop, connecting various machines and sensors into a cohesive unit. When paired with a CNC controller, it can manage auxiliary functions that fall outside the scope of pure motion control. Many users employ it to add physical control panels to their CNC setups, complete with emergency stops, spindle speed controls, and status indicators. The device’s ability to interface with temperature sensors and relays makes it equally valuable for managing coolant systems or monitoring machine health.
Beyond metalworking applications, the PoKeys57U finds use in diverse automation projects. Some makers have implemented it in custom 3D printer interfaces, where it handles everything from filament sensors to enclosure climate control. Others have created sophisticated home automation systems, using the device to coordinate lighting, security sensors, and HVAC controls. The keyboard emulation features open additional possibilities, allowing the creation of dedicated macro pads for design software or specialized input devices for industrial applications.
Intuitive Configuration for All Skill Levels
One of the most compelling aspects of the PoKeys57U is its accessible yet powerful configuration system. The accompanying software provides a graphical interface for pin assignment and basic logic configuration, making it approachable for beginners. More advanced users can leverage the built-in PoBlocks system, which offers a ladder-logic-like environment for creating complex automation sequences without traditional programming.
For those who need even greater flexibility, the device supports Lua scripting, allowing for sophisticated custom behaviors. This tiered approach to programming means that users can start simple and gradually unlock more advanced capabilities as their projects demand. The software also includes monitoring tools that provide real-time feedback on all I/O states, invaluable for debugging complex setups.
A Versatile Alternative to Conventional Solutions
While platforms like Arduino and Raspberry Pi dominate the maker scene, the PoKeys57U occupies a unique niche. It combines the plug-and-play simplicity of commercial automation controllers with the flexibility of open-ended development boards. The device’s specialized firmware handles many low-level tasks automatically, freeing users to focus on their application logic rather than driver development or communication protocols.
This specialization makes the PoKeys57U particularly valuable in scenarios where reliability and deterministic behavior are crucial. Unlike general-purpose computing platforms that must juggle multiple processes, the PoKeys57U dedicates all its resources to real-time I/O management. The result is a solution that feels more like industrial equipment than a hobbyist project, yet remains accessible and affordable for individual makers.
As we’ve seen, the PoKeys57U extends the capabilities of a CNC controller by handling peripheral automation tasks with precision and reliability. In our next exploration, we’ll discover how these same principles of control and automation can be applied to an entirely different domain – the careful cultivation of orchids in a purpose-built DIY orchidarium.
DIY Orchidarium – Where Technology Meets Horticulture
The marriage of technology and nature finds one of its most beautiful expressions in the DIY orchidarium – a carefully controlled ecosystem designed to replicate the delicate balance of an orchid’s natural habitat. Far from being just another plant enclosure, a properly constructed DIY orchidarium integrates precise environmental controls with thoughtful design to create the perfect conditions for these temperamental blooms to thrive.
The Science Behind Orchidarium Design
Creating a successful DIY orchidarium requires understanding the unique needs of epiphytic orchids. These plants don’t grow in soil but rather cling to trees in their native tropical environments, absorbing moisture and nutrients from humid air and rain. The challenge lies in recreating these conditions in a controlled space while maintaining proper air circulation to prevent fungal growth.
Modern DIY orchidarium builders employ various technological solutions to maintain this balance. Automated misting systems, often controlled by programmable timers or humidity sensors, provide regular moisture without over-saturation. Computer-controlled LED grow lights simulate the dappled sunlight of tropical canopies, with spectrum tuning to promote both vegetative growth and flowering. Some advanced setups even incorporate small computer fans controlled by temperature sensors to maintain optimal air movement.
Precision Construction Techniques
The physical construction of a DIY orchidarium demands as much attention to detail as the environmental controls. Many builders start with glass terrariums or custom-built enclosures, often incorporating CNC-cut wood or acrylic panels for precise fitting. The growing surfaces typically consist of natural or artificial bark mounts arranged at various angles to mimic tree branches, with some enthusiasts using 3D-printed custom mounts for particularly delicate species.
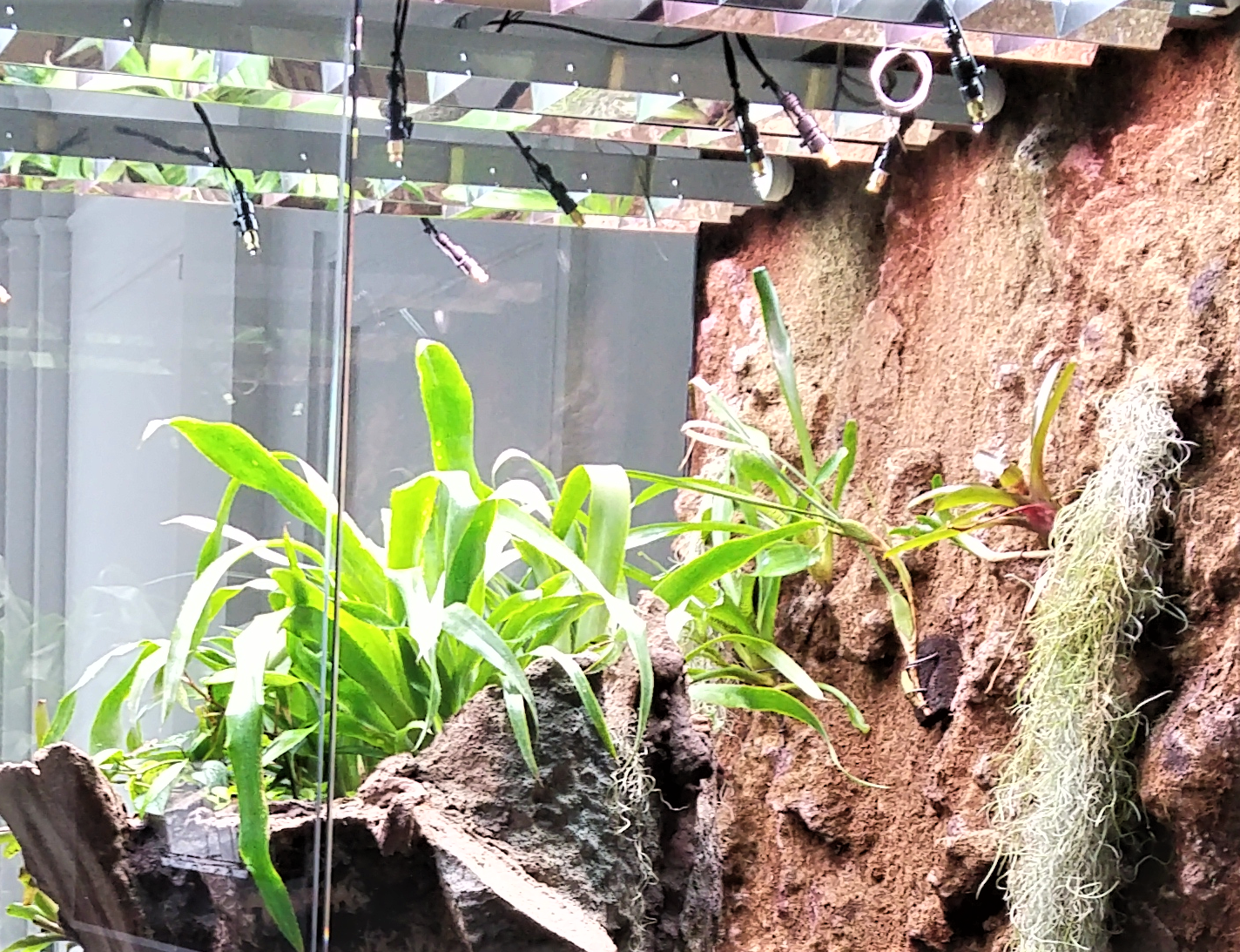

Water management systems range from simple drainage layers to sophisticated recirculating setups with automatic top-off reservoirs. The most advanced DIY orchidarium designs include secondary water features like miniature waterfalls or foggers that serve both aesthetic and functional purposes, increasing humidity while adding visual interest.
Monitoring and Automation Integration
The true potential of a DIY orchidarium emerges when incorporating modern monitoring and control systems. Many builders connect arrays of environmental sensors to microcontroller platforms that log temperature, humidity, light levels, and even substrate moisture content. This data can be used to fine-tune automatic systems or trigger alerts when conditions deviate from optimal ranges.
Some particularly tech-savvy orchid enthusiasts have taken this further by integrating their DIY orchidarium controls with home automation systems. This allows remote monitoring and adjustment of environmental conditions via smartphone apps, or even setting up automated responses like activating additional cooling fans when temperatures rise unexpectedly. The same principles used in industrial automation now help maintain the fragile balance needed for these exotic plants to flourish.
The Rewards of Custom Cultivation
Beyond the technical achievements, a well-executed DIY orchidarium offers unparalleled opportunities for plant collectors. It allows cultivation of species that would otherwise be impossible to grow in typical home environments, from high-altitude cloud forest varieties needing constant cool moisture to miniature species that would dry out instantly in normal room conditions.
The satisfaction comes not just from seeing rare orchids bloom, but from creating an entire miniature ecosystem that sustains itself with minimal intervention. Many builders find their DIY orchidarium becomes a living work of art, combining horticultural skill with engineering precision to create something greater than the sum of its parts.
As we’ve seen how technology can nurture delicate plant life, our final chapter will examine a tool that brings precision to the most practical aspects of workshop organization – the specialized flat cable cutter that ensures clean, professional results in electrical installations.
Flat Cable Cutter – The Precision Tool for Clean Cable Management
In any workshop where electronics and automation converge, proper cable management becomes essential. The flat cable cutter emerges as an unsung hero in this domain – a specialized tool designed to handle ribbon cables and flat conductors with surgical precision. Unlike conventional wire cutters that crush or fray delicate flat cables, a proper flat cable cutter delivers clean, even cuts that maintain cable integrity and ensure reliable connections.
The Engineering Behind Flat Cable Cutting
What sets a flat cable cutter apart is its unique blade geometry. The cutting edges meet at a precise angle that shears through multiple conductors simultaneously without causing the individual wires to splay or separate. This is crucial when working with modern ribbon cables that may contain dozens of fine-gauge conductors packed tightly together. The best flat cable cutter models incorporate hardened steel blades with micro-serrated edges that grip the cable during cutting, preventing the slipping that can lead to jagged edges.
Professional-grade versions often feature adjustable tension mechanisms that allow users to fine-tune the cutting pressure based on cable thickness. Some incorporate built-in length guides for repeatable cuts, while others offer interchangeable blades for different cable types – from flexible flat flex cables to more rigid ribbon varieties. The ergonomics matter just as much as the cutting mechanics, with high-quality tools balancing weight distribution to reduce hand fatigue during production work.
Applications in Automation and Electronics
The flat cable cutter proves indispensable in several workshop scenarios. When interfacing a CNC controller with peripheral devices, proper ribbon cable termination ensures signal integrity and reduces electromagnetic interference. The same applies when connecting a PoKeys57U interface board to its various sensors and actuators – a cleanly cut flat cable makes for more reliable connections in the control system.
In more specialized applications like building a DIY orchidarium’s environmental monitoring system, the flat cable cutter enables neat wiring of sensor arrays and display panels. The tool’s precision becomes particularly valuable when working with expensive components where a botched cable cut could mean scrapping an entire pre-terminated assembly. Many retro computing enthusiasts also rely on quality flat cable cutter tools when restoring vintage computer systems that use ribbon cables for internal connections.
Technique Matters: Getting the Perfect Cut
Using a flat cable cutter properly involves more than just squeezing the handles. Experienced technicians follow a specific method: First, they measure and mark the cutting point with a fine-tip marker, often using a small square to ensure perpendicular alignment. The cable gets positioned in the cutter’s jaws with just enough overhang to account for any compression during cutting. A firm, steady pressure produces the cleanest results – rapid or jerky motions can cause the individual conductors to shear at slightly different points.
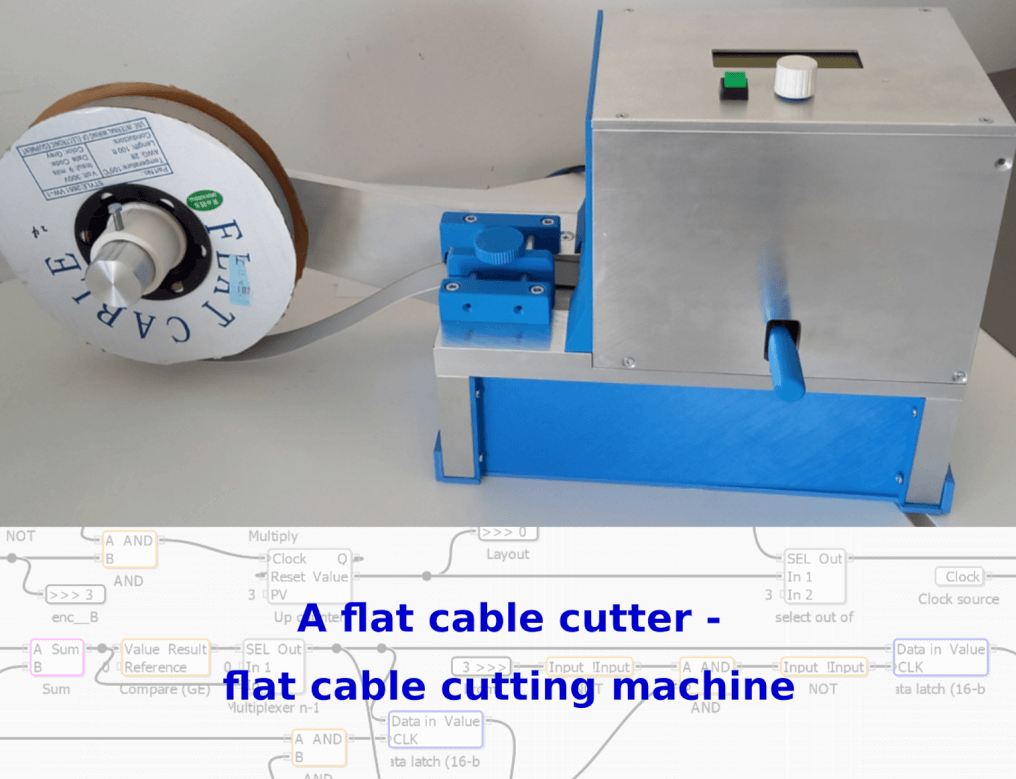
For critical applications, many professionals make a practice of inspecting each cut under magnification to verify conductor integrity. Some keep a dedicated deburring tool handy to remove any microscopic imperfections from the cut edge before installation. When working with particularly delicate cables, applying a strip of low-tack masking tape along the cut line can provide additional stability during the cutting process.
Selecting the Right Tool for the Job
Not all flat cable cutter tools are created equal. Hobbyists working with occasional ribbon cable connections might opt for an affordable entry-level model, while professional technicians handling daily cable preparations should invest in industrial-grade tools. Key selection factors include maximum cutting capacity (typically ranging from 10 to 40 conductors), blade material quality, and handle comfort for extended use.
Some specialized variants exist for particular applications. Angled-cut versions create beveled edges for easier connector insertion, while ultra-precision models with ceramic blades serve the semiconductor industry. For workshops already equipped with a CNC controller, some manufacturers even offer CNC-ground blades that maintain their edge geometry through thousands of cuts. Regardless of the specific model, a quality flat cable cutter pays for itself in reduced cable waste and more reliable connections over time.
The Unsung Hero of the Workshop
While flashier tools often grab attention, the humble flat cable cutter exemplifies how the right specialized tool can elevate work quality. In our increasingly connected workshops – where CNC controllers talk to interface boards that monitor environmental systems – maintaining clean, professional cable connections becomes more important than ever. The flat cable cutter delivers this capability with quiet efficiency, proving that sometimes the most valuable tools are those that perform one specific job exceptionally well.
As we’ve seen throughout this exploration – from the precision of CNC control to the automation capabilities of PoKeys interfaces, from the careful balance of orchidariums to the exacting cuts of cable preparation – modern making combines technological sophistication with hands-on craftsmanship. Each element plays its part in creating systems that are greater than the sum of their parts.
The Synergy of Precision Tools in Modern Creation
From the digital precision of a CNC controller to the versatile automation of PoKeys57U, from the delicate balance of a DIY orchidarium to the clean cuts of a flat cable cutter, we’ve explored how specialized tools empower makers to achieve professional-grade results. Each of these components plays a distinct yet interconnected role in modern fabrication, automation, and even horticulture.
The CNC controller stands as the cornerstone of precision manufacturing, translating digital designs into flawless physical parts. It exemplifies how software and hardware converge to achieve repeatable accuracy. The PoKeys57U extends this control, adding layers of automation and customization that transform static machines into responsive, intelligent systems. Together, they demonstrate how industrial-grade technology is now accessible to hobbyists and small-scale creators.
Meanwhile, the DIY orchidarium showcases how these same principles apply beyond traditional workshops. By integrating sensors, controlled lighting, and automated misting systems, enthusiasts replicate microclimates with scientific precision—proving that technology can nurture nature as effectively as it shapes metal or plastic.
Finally, the flat cable cutter reminds us that even the smallest details matter. Clean, precise cuts ensure reliable connections in electronics, automation, and beyond. It’s a testament to how the right tool—no matter how simple—can elevate craftsmanship from functional to exceptional.
The Future of Making
As these tools evolve, their integration will only deepen. Imagine a CNC controller automatically adjusting toolpaths based on sensor feedback from a PoKeys57U, while a DIY orchidarium nearby self-regulates using the same automation principles. The flat cable cutter, in turn, ensures every connection in this ecosystem remains flawless.
This is the new era of creation—where precision engineering, smart automation, and artistic vision intersect. Whether you’re machining parts, automating a workshop, cultivating rare orchids, or perfecting cable management, the right tools make all the difference. The only limit is imagination.
